Prepare for success in geometry with our comprehensive Geometry Chapter 2 Practice Test. Covering key concepts and skills, this practice test will help you identify areas for improvement and boost your confidence for the exam.
This practice test provides a thorough overview of the essential concepts covered in Chapter 2, including angles, triangles, and transformations. By completing the practice problems and reviewing the solutions, you’ll reinforce your understanding and gain valuable experience in applying these concepts.
Geometry Chapter 2 Practice Test
The Geometry Chapter 2 Practice Test is designed to help you assess your understanding of the concepts covered in Chapter 2. It is an opportunity for you to identify areas where you may need additional support and to prepare for the upcoming chapter test.
The practice test covers the following topics:
- Lines and angles
- Triangles
- Quadrilaterals
- Circles
To prepare for the practice test, it is important to review the material covered in Chapter 2 and to complete the practice problems at the end of each section. You may also want to consider working with a tutor or joining a study group.
Concepts Assessed in the Practice Test: Geometry Chapter 2 Practice Test
The Geometry Chapter 2 Practice Test assesses your understanding of fundamental geometric concepts and skills. Mastery of these concepts is crucial for success in Geometry, as they form the foundation for more advanced topics.
The practice test covers the following key concepts:
Lines and Angles
- Identifying and classifying different types of lines and angles (e.g., parallel, perpendicular, complementary)
- Measuring and calculating angle measures using protractors and angle relationships
- Applying properties of lines and angles to solve problems involving angle bisectors, perpendicular bisectors, and parallel lines
Triangles
- Identifying and classifying different types of triangles (e.g., equilateral, isosceles, right)
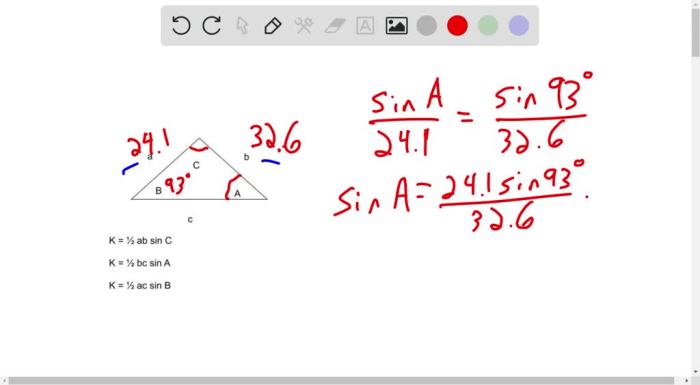
- Solving problems involving triangle congruence, similarity, and area
li>Understanding the relationships between the sides and angles of triangles (e.g., Pythagorean theorem, sine and cosine laws)
Polygons
- Identifying and classifying different types of polygons (e.g., quadrilateral, pentagon, hexagon)
- Calculating the perimeter and area of polygons
- Understanding the properties of regular polygons (e.g., symmetry, angles)
Circles
- Identifying and classifying different parts of a circle (e.g., radius, diameter, circumference)
- Calculating the circumference and area of circles
- Solving problems involving tangents, secants, and chords
Practice Problems and Solutions
This section provides a variety of practice problems to reinforce the concepts covered in Chapter 2. Each problem is followed by a detailed solution to help you understand the steps involved in solving the problem.
The problems cover a range of topics, including angle relationships, parallel lines, and triangles.
Angle Relationships
- Problem 1: Find the value of x in the following diagram:
- Solution: The sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 degrees. Therefore, we have:
- Problem 2: Find the value of y in the following diagram:
- Solution: Vertical angles are equal. Therefore, we have:

x + 50° + 70° = 180°
x = 180°- 50° – 70°
x = 60°

y = 110°
Parallel Lines
- Problem 3: Find the value of x in the following diagram:
- Solution: Alternate interior angles are equal. Therefore, we have:
- Problem 4: Find the value of y in the following diagram:
- Solution: Corresponding angles are equal. Therefore, we have:

x = 60°

y = 120°
Triangles
- Problem 5: Find the area of a triangle with a base of 10 cm and a height of 8 cm.
- Solution: The area of a triangle is given by the formula:
- Problem 6: Find the perimeter of a triangle with sides of length 5 cm, 7 cm, and 9 cm.
- Solution: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its sides. Therefore, we have:
Area = (1/2)- base – height
Area = (1/2)- 10 cm – 8 cm
Area = 40 cm²
Perimeter = 5 cm + 7 cm + 9 cm
Perimeter = 21 cm
Strategies for Answering Practice Questions
To excel in the geometry chapter 2 practice test, adopting effective strategies for answering practice questions is crucial. Understanding the question stem and answer choices, along with the ability to eliminate incorrect options, are key components of a successful approach.
Understanding the Question Stem and Answer Choices, Geometry chapter 2 practice test
Before attempting to answer a multiple-choice question, it’s essential to thoroughly comprehend the question stem. This involves identifying the main concept being tested and the specific information required to answer it. Additionally, carefully examine each answer choice, paying attention to the wording and any subtle differences that may impact the correctness of the option.
Eliminating Incorrect Answer Choices
To narrow down the possible correct answers, employ the strategy of eliminating incorrect choices. Begin by identifying options that are clearly incorrect or irrelevant to the question. This can be achieved by checking for logical inconsistencies, factual errors, or statements that contradict the given information.
By eliminating incorrect answer choices, you increase the probability of selecting the correct option.
Time Management and Test-Taking Tips
Effective time management is crucial during the practice test to ensure you complete all questions within the allocated time. Here are some strategies to help you pace yourself and prioritize questions.
Pacing Yourself
- Allocate a specific amount of time to each question or section.
- Start with the questions you are most confident about.
- Move on to more challenging questions if time permits.
Prioritizing Questions
- Identify the questions that carry the most weightage.
- Focus on completing those questions first.
- If you encounter a particularly difficult question, skip it for now and return to it later.
Staying Calm and Focused
- Take deep breaths to reduce stress and improve focus.
- Stay positive and avoid dwelling on mistakes.
- Remind yourself that this is just a practice test and use it as an opportunity to learn and improve.
Using the Practice Test for Improvement
The practice test serves as a diagnostic tool, highlighting areas where you excel and those requiring improvement. By carefully analyzing your results, you can pinpoint specific concepts or skills that need attention.
When reviewing your mistakes, focus on understanding why they occurred. Was it a lack of understanding of the concept, a careless error, or a time constraint issue? Once you identify the root cause, you can develop targeted strategies to address the problem.
Setting Goals and Creating a Study Plan
Based on your practice test results, set realistic goals for improvement. Prioritize the areas where you need the most support and allocate more study time to them. Create a structured study plan that includes dedicated time for reviewing concepts, practicing problems, and seeking additional help if needed.
Clarifying Questions
What concepts are covered in the Geometry Chapter 2 Practice Test?
The practice test covers key concepts from Chapter 2, including angles, triangles, and transformations.
How can I use the practice test to improve my geometry skills?
By completing the practice problems and reviewing the solutions, you can identify areas for improvement and focus your studies accordingly.
Is the practice test suitable for all levels of geometry students?
Yes, the practice test is designed to be accessible to students of all levels, providing both review and challenge.