Billings in excess of costs journal entry is a critical accounting concept that requires a thorough understanding for accurate financial reporting. This guide will delve into the intricacies of this journal entry, providing a comprehensive overview of its definition, purpose, recording procedures, and implications for financial statements.
Billings in excess of costs arise when a company bills its customers an amount greater than the actual costs incurred to provide the goods or services. Understanding the proper accounting treatment for such transactions is essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of financial records.
Definition of Billings in Excess of Costs
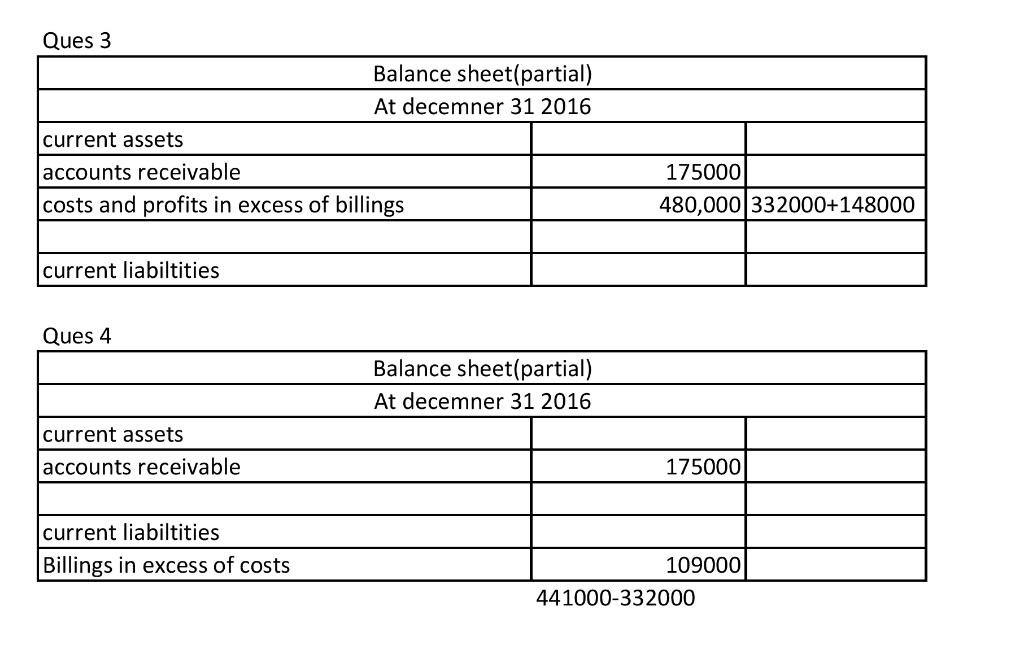
Billings in excess of costs represent amounts billed to customers that exceed the actual costs incurred in providing the goods or services. This situation arises when a company estimates the costs of a project or service and bills the customer based on the estimate, but the actual costs turn out to be lower than the estimate.
The purpose of recording billings in excess of costs is to recognize the revenue earned and to defer the recognition of the excess amount until the actual costs are incurred.
Journal Entry for Billings in Excess of Costs
The journal entry to record billings in excess of costs is as follows:
Debit: Accounts Receivable
Credit: Billings in Excess of Costs
Credit: Revenue
The Accounts Receivable account is debited for the amount billed to the customer.
The Billings in Excess of Costs account is credited for the excess amount billed over the actual costs incurred.
The Revenue account is credited for the amount of revenue earned.
This journal entry has the following impact on the financial statements:
- Assets (Accounts Receivable) increase.
- Liabilities (Billings in Excess of Costs) increase.
- Equity (Revenue) increases.
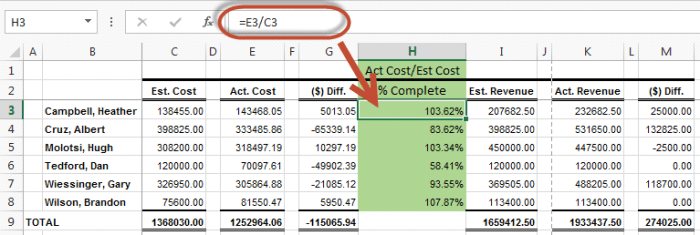
Methods for Calculating Billings in Excess of Costs: Billings In Excess Of Costs Journal Entry
There are two main methods for calculating billings in excess of costs:
- Percentage of Completion Method: Under this method, billings are based on the percentage of the project that has been completed.
- Cost-to-Cost Method: Under this method, billings are based on the actual costs incurred to date.
The percentage of completion method is more conservative than the cost-to-cost method because it recognizes revenue only as the project is completed.
Examples of Billings in Excess of Costs
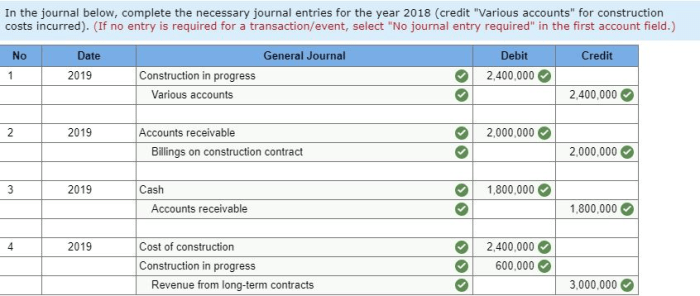
Examples of situations where billings in excess of costs may occur include:
- Long-term construction projects: In these projects, the costs may be incurred over several years, while the billings are based on the estimated total cost of the project.
- Service contracts: In these contracts, the company may bill the customer for the estimated cost of the services to be provided over the term of the contract.
In both of these cases, the company would record billings in excess of costs to defer the recognition of the excess amount until the actual costs are incurred.
Reporting and Disclosure of Billings in Excess of Costs
Billings in excess of costs must be reported on the balance sheet as a liability.
The following disclosures are required in the financial statements:
- The amount of billings in excess of costs.
- The method used to calculate billings in excess of costs.
- The nature of the transactions that gave rise to the billings in excess of costs.
Audit Considerations for Billings in Excess of Costs
Auditors should perform the following procedures to verify the accuracy of billings in excess of costs:
- Review the contracts and other documentation to determine the basis for the billings.
- Compare the billings to the actual costs incurred.
- Assess the reasonableness of the estimated costs.
Auditors should also be aware of the potential risks associated with billings in excess of costs, such as:
- Overstatement of revenue: Billings in excess of costs can lead to an overstatement of revenue if the actual costs incurred exceed the estimated costs.
- Understatement of expenses: Billings in excess of costs can lead to an understatement of expenses if the excess amount is not recognized as a liability.
Helpful Answers
What is the purpose of recording billings in excess of costs?
The purpose of recording billings in excess of costs is to recognize revenue when it is earned, even if the related costs have not yet been incurred. This ensures that the company’s financial statements accurately reflect its economic activities.
How does the journal entry for billings in excess of costs affect the financial statements?
The journal entry for billings in excess of costs increases the asset account (Accounts Receivable) and the income statement account (Revenue). This results in an increase in both the company’s assets and its net income.
What are the different methods for calculating billings in excess of costs?
There are two common methods for calculating billings in excess of costs: the percentage-of-completion method and the completed-contract method. The percentage-of-completion method recognizes revenue based on the percentage of work completed, while the completed-contract method recognizes revenue only when the contract is complete.