Match the lymphatic organ with its function and delve into the intricate workings of the lymphatic system, a crucial component of our immune defense. From the lymph nodes that filter lymph to the spleen that purifies blood, each organ plays a vital role in maintaining our health.
This comprehensive guide will provide an in-depth understanding of the functions of the major lymphatic organs, empowering you with the knowledge to appreciate the remarkable complexity of the human body.
Lymphatic Organs and Their Functions: Match The Lymphatic Organ With Its Function

The lymphatic system is a network of organs, tissues, and vessels that plays a vital role in the body’s immune defense and fluid balance. Major lymphatic organs include lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, Peyer’s patches, and the appendix, each with specific functions in the lymphatic system.
Lymph Node Function
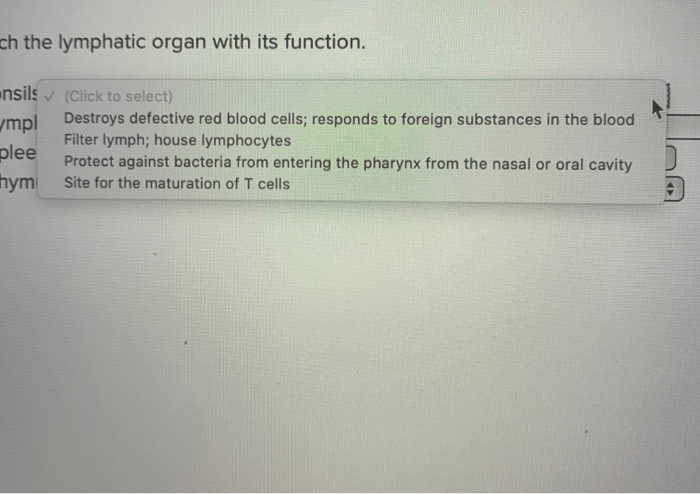
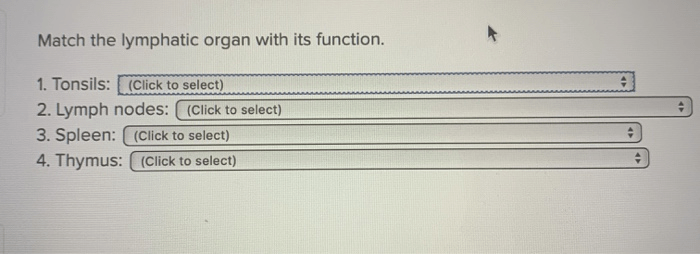
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures located throughout the body that filter and purify lymph. They contain immune cells that trap and destroy pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses, preventing their spread throughout the body.
Lymph nodes also play a crucial role in the immune response by initiating an adaptive immune response. When antigens (foreign substances) are detected in the lymph, immune cells in the lymph nodes activate and proliferate, producing antibodies and memory cells that target specific pathogens.
Spleen Function
The spleen is a large, fist-sized organ located in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen. It filters blood, removing old or damaged red blood cells and other cellular debris. The spleen also contains immune cells that help detect and destroy pathogens.
Additionally, the spleen serves as a reservoir for red blood cells. In times of stress or need, the spleen can contract and release red blood cells into the bloodstream, increasing oxygen-carrying capacity.
Thymus Function
The thymus is a small, triangular organ located in the upper chest. It plays a crucial role in the development and maturation of T lymphocytes (T cells), a type of white blood cell essential for cell-mediated immunity.
In the thymus, immature T cells undergo a selection process where they are tested for self-tolerance. T cells that react against the body’s own tissues are eliminated, preventing autoimmune diseases.
Tonsils Function
Tonsils are small, oval-shaped structures located at the back of the throat. They trap and filter pathogens that enter through the mouth or nose, preventing their entry into the respiratory tract.
Tonsils also contain immune cells that initiate immune responses against pathogens. They produce antibodies and activate other immune cells to fight infections.
Peyer’s Patches Function
Peyer’s patches are small, lymphoid structures located in the small intestine. They play a vital role in the immune response against pathogens in the digestive tract.
Peyer’s patches contain immune cells that detect and destroy pathogens present in the gut. They also initiate an immune response by producing antibodies and activating other immune cells.
Appendix Function, Match the lymphatic organ with its function
The appendix is a small, finger-like structure attached to the large intestine. Its function in the lymphatic system is still not fully understood, but it is believed to play a role in immune function and gut microbiota.
The appendix contains lymphoid tissue that may contribute to immune surveillance and the production of immune cells. Additionally, it is thought to harbor beneficial gut bacteria that may play a role in maintaining gut health.
FAQ
What is the primary function of lymph nodes?
Lymph nodes act as filters, trapping pathogens and cellular debris from the lymph fluid, contributing to the body’s immune response.
How does the spleen contribute to immune function?
The spleen serves as a filter for blood, removing old or damaged red blood cells and producing antibodies that enhance the immune system’s ability to combat infections.
What is the role of the thymus in the lymphatic system?
The thymus plays a crucial role in the development and maturation of T lymphocytes, which are essential for cell-mediated immunity.