A biologist measures the allele frequency apex, delving into the intricate relationship between apex predators and the genetic diversity of their prey populations. This exploration unveils the profound influence of these top-tier predators on the evolutionary trajectory of their prey, shaping the genetic makeup of entire ecosystems.
Through a meticulous examination of allele frequencies, scientists unravel the complex interplay between predator and prey, shedding light on the forces that drive genetic variation and adaptation. This knowledge serves as a cornerstone for conservation efforts, guiding strategies to protect and preserve the delicate balance of nature.
Allele Frequency Measurement Techniques: A Biologist Measures The Allele Frequency Apex
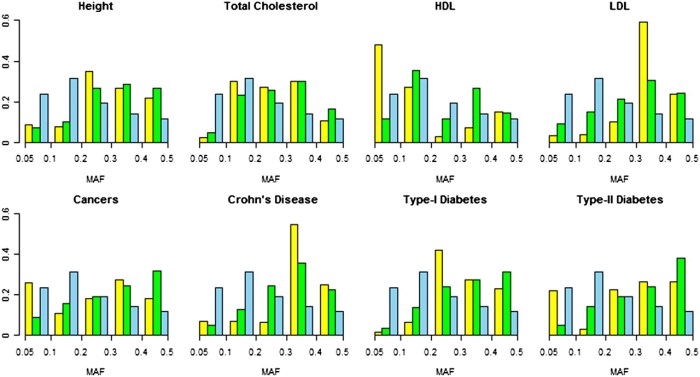
Allele frequencies, representing the proportion of different alleles within a population, are crucial for understanding genetic diversity and evolutionary processes. Accurately measuring allele frequencies requires specific techniques.
Gel electrophoresis, a fundamental technique, separates DNA fragments based on size and charge. It allows researchers to visualize and quantify alleles, providing insights into their relative abundance.
PCR-based methods, such as PCR-RFLP (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) and ARMS (Amplification Refractory Mutation System), amplify specific DNA regions and detect variations associated with different alleles. These methods offer high sensitivity and specificity.
Sequencing technologies, including Sanger sequencing and next-generation sequencing, provide comprehensive information about DNA sequences, enabling the identification and quantification of alleles. These methods offer high accuracy and resolution.
Apex Predators and Allele Frequency
Apex predators, occupying the top of food chains, can exert substantial influence on the genetic diversity of prey populations.
By selectively targeting individuals with specific alleles, apex predators can alter allele frequencies in prey populations. This selective pressure can favor certain alleles that enhance prey survival in the presence of predators.
For instance, in bighorn sheep populations, wolves preferentially prey on individuals with specific immune system alleles, leading to a shift in allele frequencies that enhances resistance to parasites.
Applications of Allele Frequency Data
Allele frequency data finds applications in diverse fields, including population genetics, conservation biology, and evolutionary studies.
In population genetics, allele frequencies provide insights into genetic diversity, population structure, and evolutionary processes. By tracking allele frequency changes over time, researchers can monitor genetic drift and the impact of selection.
In conservation biology, allele frequency data helps identify genetically distinct populations, assess genetic diversity within endangered species, and inform conservation strategies.
In evolutionary studies, allele frequency data allows researchers to infer evolutionary relationships, study the origins of species, and investigate the role of natural selection in shaping genetic variation.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
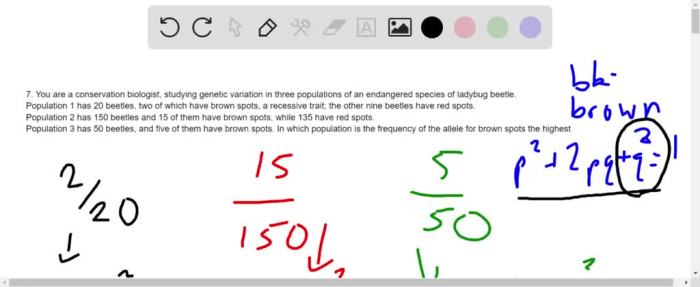
Analyzing allele frequency data involves statistical methods to estimate allele frequencies and test for deviations from expected values.
Chi-square tests, for example, assess whether observed allele frequencies differ significantly from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, a theoretical model of allele frequencies in non-evolving populations.
Other statistical tests, such as F-statistics, measure genetic differentiation among populations and estimate the proportion of genetic variation within and between populations.
Interpreting allele frequency data requires careful consideration of potential sources of error and bias, such as sampling error, mutation, and gene flow. Researchers must also account for the influence of non-genetic factors, such as environmental conditions and population history.
FAQ Section
What are the key techniques used to measure allele frequencies?
Gel electrophoresis, PCR-based methods, and sequencing are commonly employed techniques for measuring allele frequencies.
How do apex predators influence the allele frequencies of prey populations?
Apex predators can exert selective pressure on prey populations, favoring individuals with certain advantageous alleles, thereby altering the allele frequencies over time.
What are some applications of allele frequency data in conservation biology?
Allele frequency data aids in identifying genetically distinct populations, assessing genetic diversity, and informing conservation strategies to preserve endangered species.