Orbitals and orbital notation homework answers – Embark on an illuminating journey into the realm of orbitals and orbital notation, where the foundations of atomic structure unravel. This comprehensive guide unveils the intricacies of atomic orbitals, their significance in understanding atomic behavior, and the rules that govern their filling.
Delve into the concepts of Aufbau principle and Hund’s rule, exploring their profound impact on electron configurations.
Discover the concept of orbital energy levels and delve into the factors that influence their energy. Witness the fascinating phenomenon of orbital hybridization and its pivotal role in molecular bonding. With a wealth of examples and insightful explanations, this guide empowers you to master the intricacies of orbitals and orbital notation, unlocking the gateway to a deeper understanding of atomic chemistry.
Orbitals and Orbital Notation: Orbitals And Orbital Notation Homework Answers

Atomic orbitals are the three-dimensional regions around the nucleus of an atom where electrons are most likely to be found. They are characterized by their shape, orientation, and energy level. The different types of atomic orbitals are designated by the letters s, p, d, and f.
The s orbitals are spherical in shape, the p orbitals are dumbbell-shaped, the d orbitals have more complex shapes, and the f orbitals are even more complex.
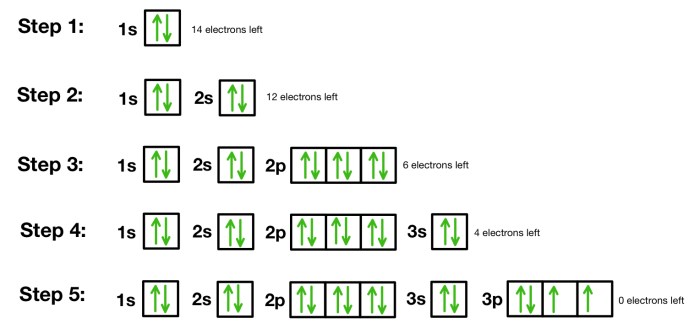
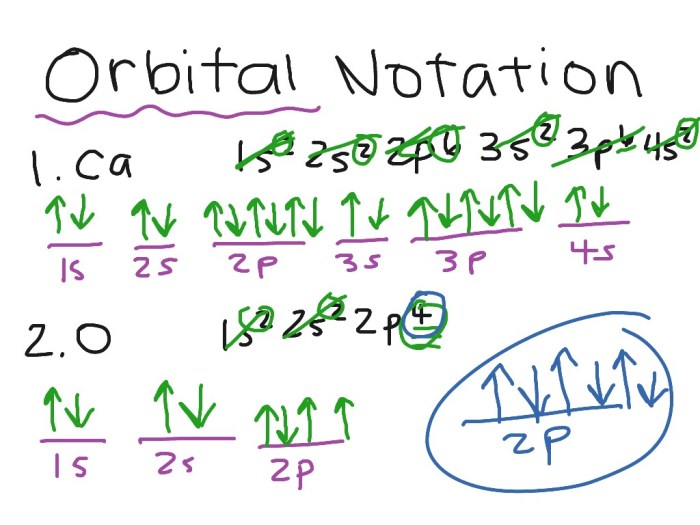
Orbital notation is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. It uses the symbols for the atomic orbitals to indicate the number of electrons in each orbital. For example, the electron configuration of helium can be written as 1s 2, which means that there are two electrons in the 1s orbital.
Aufbau Principle and Hund’s Rule
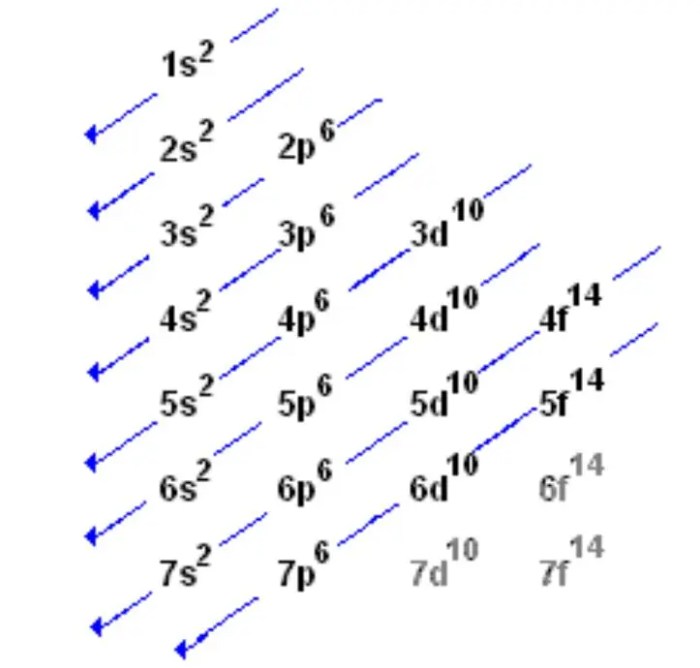
The Aufbau principle states that electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first. Hund’s rule states that when there are multiple orbitals of equal energy, electrons will occupy them singly with parallel spins before pairing up.
Orbital Energy Levels
The energy of an orbital is determined by its shape and orientation. The s orbitals have the lowest energy, followed by the p orbitals, the d orbitals, and the f orbitals. The energy of an orbital also increases with the atomic number of the element.
Orbital Hybridization, Orbitals and orbital notation homework answers
Orbital hybridization is the process of combining two or more atomic orbitals to form a new orbital with a different shape and energy level. The most common types of hybrid orbitals are the sp, sp 2, and sp 3orbitals. These hybrid orbitals are used to form the bonds in molecules.
FAQ Compilation
What is an atomic orbital?
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of electrons in an atom. It defines the region of space where an electron is most likely to be found.
What is the significance of orbital notation?
Orbital notation provides a concise and systematic way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. It indicates the number and arrangement of electrons in different atomic orbitals.
What is the Aufbau principle?
The Aufbau principle states that electrons fill atomic orbitals in order of increasing energy. Lower energy orbitals are filled before higher energy orbitals.
What is Hund’s rule?
Hund’s rule states that when filling orbitals of equal energy, electrons will occupy separate orbitals with parallel spins before pairing up with opposite spins.