Match the characteristics to the correct phylum. – Match the Characteristics to the Correct Phylum takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with an authoritative tone into a world crafted with knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
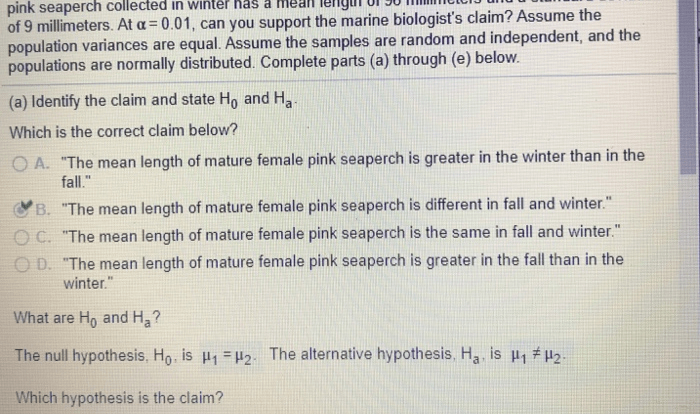
The diverse array of organisms inhabiting our planet can be classified into distinct groups based on their shared characteristics. Phyla, the highest level of taxonomic classification, represent major divisions within the animal kingdom. Understanding the defining features of each phylum is crucial for unraveling the intricate tapestry of life’s evolutionary history.
Characteristics of Phyla

Phyla are the primary taxonomic ranks used to classify living organisms. They are characterized by a distinct set of morphological, physiological, and genetic features that distinguish them from other phyla.
Key characteristics used to differentiate phyla include:
- Body plan (e.g., symmetry, segmentation)
- Tissue organization (e.g., presence of true tissues)
- Locomotion (e.g., swimming, crawling, flying)
- Feeding mechanisms (e.g., filter feeding, predation)
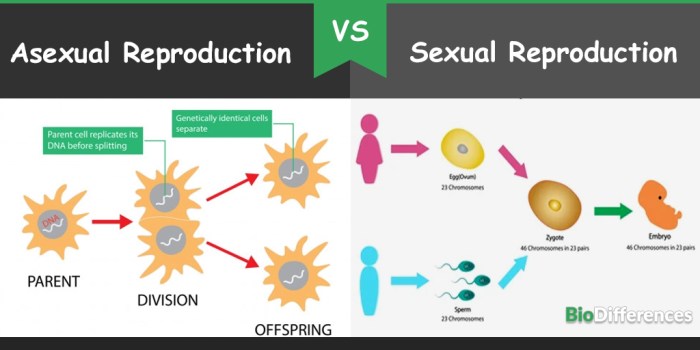
- Reproduction (e.g., sexual, asexual)
- Genetic makeup (e.g., number and structure of chromosomes)
By examining these characteristics, scientists can identify and classify organisms into their respective phyla.
Matching Characteristics to Phyla: Match The Characteristics To The Correct Phylum.
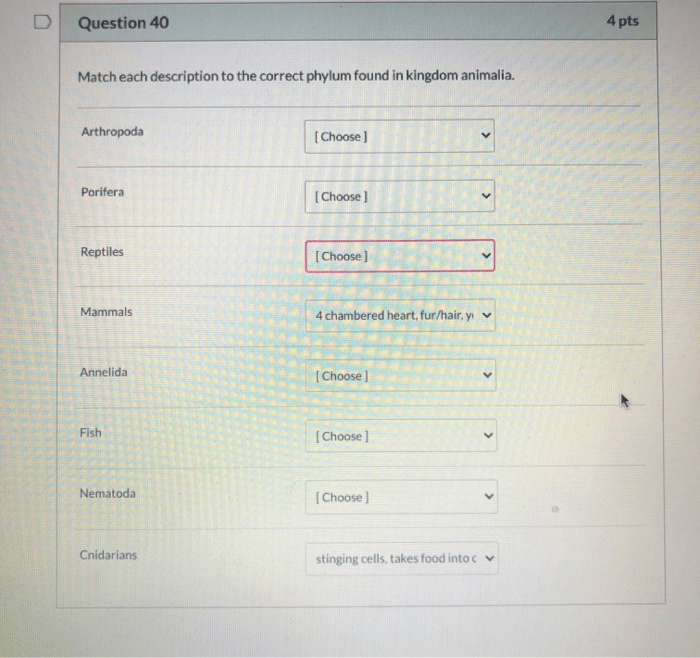
The following table summarizes the key characteristics and representative organisms of different phyla:
| Phylum | Characteristics | Representative Organisms |
|---|---|---|
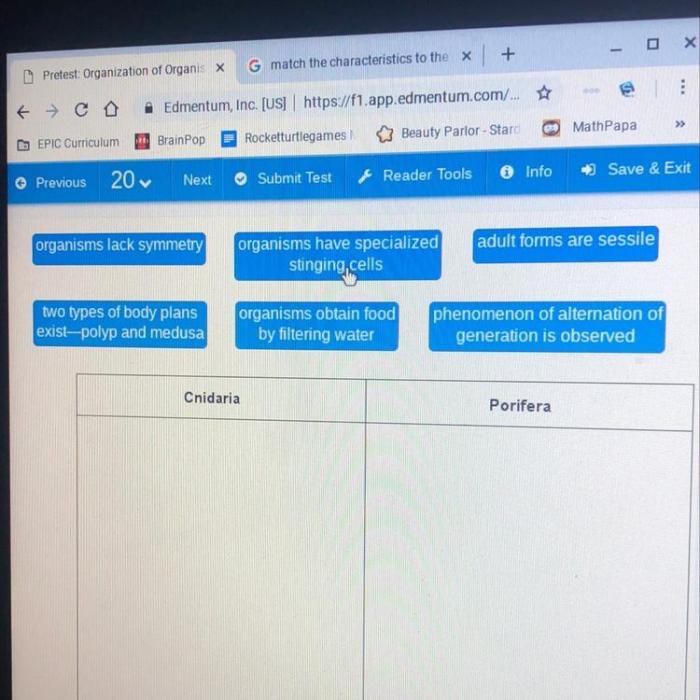
| Porifera | – Asymmetrical, sessile | – Sponges |
| Cnidaria | – Radial symmetry, stinging cells | – Jellyfish, corals |
| Platyhelminthes | – Bilaterally symmetrical, flattened | – Flatworms |
| Nematoda | – Bilaterally symmetrical, roundworms | – Roundworms |
| Annelida | – Bilaterally symmetrical, segmented | – Earthworms, leeches |
| Mollusca | – Bilaterally symmetrical, soft-bodied | – Snails, clams, octopuses |
| Arthropoda | – Bilaterally symmetrical, jointed appendages | – Insects, spiders, crabs |
| Echinodermata | – Radial symmetry, water vascular system | – Starfish, sea urchins |
| Chordata | – Bilaterally symmetrical, notochord | – Fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals |
Identification and Classification
Organisms are identified and classified into phyla based on their morphological and molecular characteristics. Comparative anatomy examines the physical structures of organisms to identify similarities and differences. Molecular data, such as DNA sequences, provides insights into genetic relationships between organisms.
The following steps are typically involved in identifying and classifying organisms:
- Collection of specimens
- Examination of morphological features
- Extraction and analysis of DNA
- Comparison of data to known taxa
- Assignment to a specific phylum
Evolutionary Relationships
Phyla are believed to have evolved from a common ancestor over millions of years. Evidence supporting this includes:
- Similarities in basic body plans
- Shared genetic sequences
- Fossil records
The hierarchical classification system groups phyla into larger categories based on their evolutionary relationships. For example, the phylum Chordata is divided into subphyla such as Vertebrata and Tunicata.
Phylogenetic Analysis
Phylogenetic analysis is used to reconstruct the evolutionary history of organisms. Techniques such as cladistics, parsimony, and maximum likelihood are employed to analyze phylogenetic data.
Cladistics focuses on shared derived characters, while parsimony seeks to find the simplest explanation for evolutionary relationships. Maximum likelihood uses statistical methods to estimate the probability of different evolutionary trees.
The resulting phylogenetic tree represents the hypothesized evolutionary relationships between different phyla, providing insights into the origins and diversification of life on Earth.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the significance of matching characteristics to the correct phylum?
Matching characteristics to the correct phylum is essential for understanding the diversity of life and the evolutionary relationships between different organisms.
How are organisms classified into phyla?
Organisms are classified into phyla based on shared morphological, physiological, and genetic characteristics.
What techniques are used to identify and classify organisms into phyla?
Comparative anatomy, molecular data analysis, and phylogenetic studies are commonly used techniques for identifying and classifying organisms into phyla.