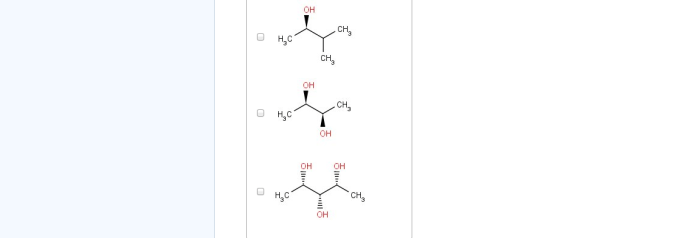
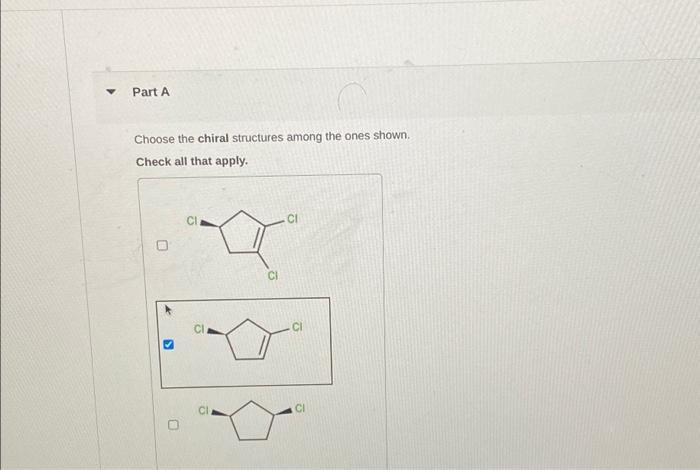
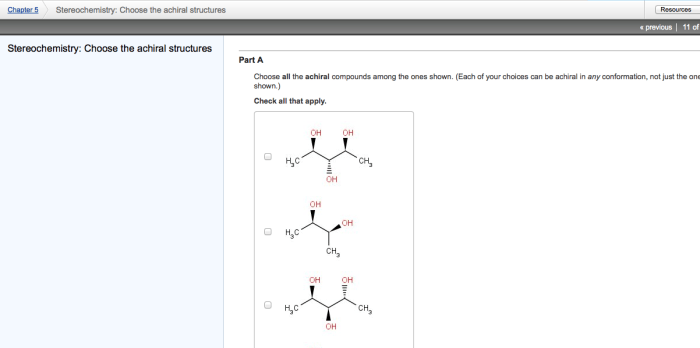
Embark on a journey into the fascinating realm of chirality, where molecules mirror each other like intricate reflections. Choose the chiral structures among the ones shown, and delve into a world of asymmetry and molecular recognition. From pharmaceuticals to materials science, chirality plays a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of the molecular world.
This comprehensive guide unravels the complexities of chirality, empowering you to identify and manipulate chiral structures with precision. Explore the fundamental concepts, delve into the methods for identifying chirality, and uncover the techniques used to separate enantiomers.
Stereochemistry and Chirality
Stereochemistry is the study of the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms and groups in a molecule. Chirality is a property of molecules that lack symmetry and cannot be superimposed on their mirror image. Chiral molecules exist in two forms, known as enantiomers, which are mirror images of each other but are not superimposable.
Enantiomers have identical physical and chemical properties, except for their interaction with polarized light. One enantiomer rotates plane-polarized light clockwise, while the other rotates it counterclockwise. This property is known as optical activity and is used to identify and characterize chiral molecules.
Methods for Identifying Chiral Structures, Choose the chiral structures among the ones shown
- Optical Activity:Measuring the rotation of plane-polarized light by a sample can determine the chirality of a molecule.
- NMR Spectroscopy:NMR spectroscopy can distinguish between enantiomers by examining the different chemical shifts of their nuclei.
- X-ray Crystallography:X-ray crystallography can provide direct evidence of the three-dimensional structure of a molecule, including its chirality.
Chiral Resolution Techniques: Choose The Chiral Structures Among The Ones Shown
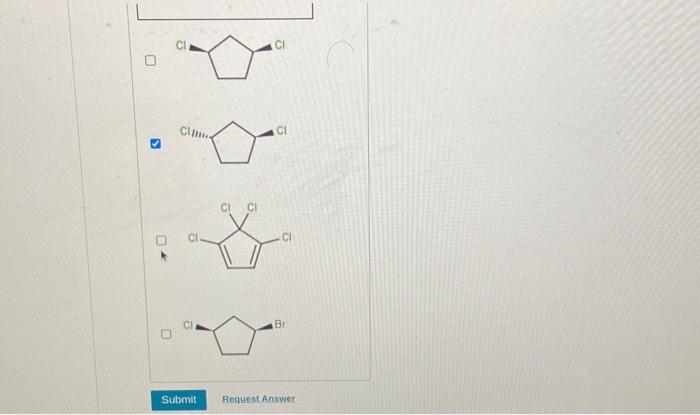
Chiral resolution is the process of separating enantiomers from a mixture. Several techniques can be used for this purpose, including:
- Chiral Chromatography:This technique uses a chiral stationary phase to separate enantiomers based on their different interactions with the stationary phase.
- Chiral Crystallization:This technique relies on the formation of diastereomeric crystals, which are crystals that contain two different enantiomers in a fixed ratio.
- Enzymatic Resolution:This technique uses enzymes to selectively react with one enantiomer, leaving the other enantiomer unreacted.
Applications of Chiral Compounds
Chiral compounds have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Pharmaceuticals:Many drugs are chiral, and their enantiomers can have different pharmacological properties. It is crucial to separate and use the correct enantiomer for optimal efficacy and safety.
- Agrochemicals:Pesticides and herbicides can be chiral, and their enantiomers can have different biological activities. Enantioselective synthesis is essential for developing environmentally friendly and effective agrochemicals.
- Materials Science:Chiral materials have unique properties that make them useful in various applications, such as optics, electronics, and catalysis.
Design and Synthesis of Chiral Molecules
Several strategies can be employed to design and synthesize chiral molecules:
- Chiral Auxiliaries:These are chiral molecules that can be temporarily attached to a substrate to induce chirality during a reaction.
- Chiral Catalysts:These are catalysts that contain chiral ligands and can promote enantioselective reactions.
- Asymmetric Reactions:These are reactions that produce one enantiomer in excess over the other. They can be achieved using chiral catalysts or chiral reagents.
Essential Questionnaire
What is chirality?
Chirality is a property of molecules that lack mirror symmetry, meaning they cannot be superimposed on their mirror images.
How can I identify chiral structures?
Various methods can be used to identify chiral structures, including optical activity, NMR spectroscopy, and X-ray crystallography.
What are enantiomers?
Enantiomers are mirror-image isomers of chiral molecules, having the same molecular formula but different spatial arrangements.
How can I separate enantiomers?
Techniques such as chiral chromatography, chiral crystallization, and enzymatic resolution can be employed to separate enantiomers.
What are the applications of chiral compounds?
Chiral compounds find applications in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science.