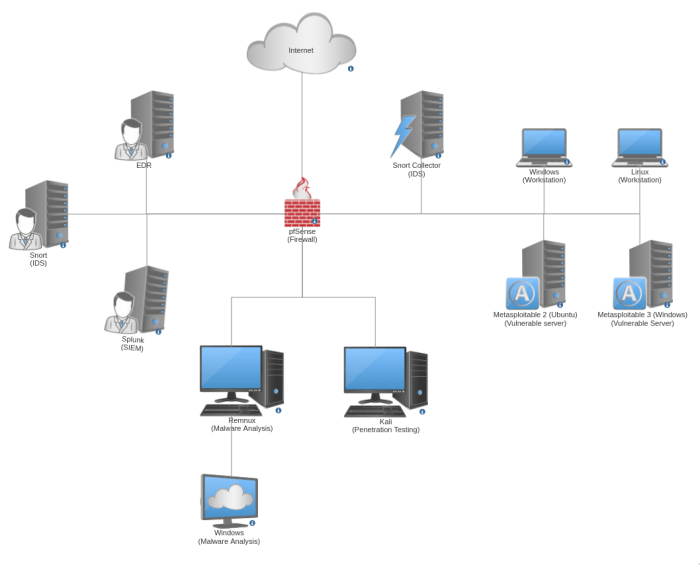
Embark on a captivating journey with Lab 14-1 setup host security, where you’ll delve into the intricacies of safeguarding your digital fortress. Discover the secrets of impenetrable host security, unravel common threats, and emerge as a cyber guardian with an arsenal of tools and techniques.
As you navigate this comprehensive guide, you’ll uncover the principles of host security, master the art of configuring security settings, and explore the latest security tools. Prepare to test and monitor your defenses, ensuring your digital domain remains impregnable.
Understanding Lab 14-1 Setup Host Security

Lab 14-1 Setup Host Security aims to enhance your understanding of host security principles and practices. It guides you through configuring and managing host security measures to protect your systems from potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Key Concepts and Principles
Host security involves safeguarding individual computers or servers from unauthorized access, malicious software, and other threats. It encompasses various aspects, including:
Access control
Managing who can access the host and what they can do.
Vulnerability management
Identifying and patching security flaws to prevent exploitation.
Intrusion detection
Monitoring for suspicious activity and detecting potential attacks.
Incident response
Responding to and recovering from security breaches.
Make sure you’re all set up for Lab 14-1 and have your host security in check. If you’re looking for some extra guidance, check out the Zeta Phi Beta final test for some helpful tips. Once you’ve reviewed the material, come back to Lab 14-1 and ace your host security setup.
Common Threats and Vulnerabilities, Lab 14-1 setup host security
Lab 14-1 addresses common threats and vulnerabilities that can compromise host security, such as:
Malware
Malicious software that can damage or steal data, disrupt operations, or spy on users.
Phishing
Attempts to trick users into revealing sensitive information by sending fraudulent emails or messages.
Unpatched vulnerabilities
Security flaws in software or systems that can be exploited by attackers.
Weak passwords
Passwords that are easy to guess or crack, providing attackers with easy access to systems.
Social engineering
Exploiting human vulnerabilities to manipulate users into taking actions that compromise security.By understanding these threats and vulnerabilities, you can develop effective host security measures to protect your systems and data.
Configuring Host Security Settings
Configuring host security settings is crucial for protecting your systems from unauthorized access and malicious attacks. In this lab, you will learn how to configure various security settings to enhance the security posture of your host systems.
The following are some of the key security settings that you should configure:
- Firewall settings
- User account settings
- Password policies
- Software update settings
By configuring these settings appropriately, you can significantly reduce the risk of security breaches and protect your host systems from unauthorized access.
Firewall Settings
A firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. It acts as a barrier between your host system and the external network, allowing only authorized traffic to pass through.
When configuring firewall settings, it is important to:
- Enable the firewall
- Create firewall rules to allow only necessary traffic
- Block all other traffic
By following these steps, you can ensure that only authorized traffic is allowed to enter or leave your host system, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and malicious attacks.
Installing and Configuring Security Tools
Ensuring host security involves employing a range of security tools to protect against various threats. These tools provide comprehensive protection, enabling the detection and prevention of unauthorized access, malware, and other security breaches.
Antivirus and Anti-malware Software
Antivirus and anti-malware software are essential for detecting and removing malicious software, such as viruses, worms, and Trojans. They continuously scan files, emails, and network traffic for suspicious activity, preventing infections and protecting sensitive data.
To install antivirus software in the lab environment, follow these steps:
- Download the antivirus software from a reputable vendor.
- Run the installation wizard and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Configure the antivirus settings to ensure regular scans and automatic updates.
Firewalls
Firewalls are network security systems that monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. They prevent unauthorized access to the host by blocking malicious traffic and enforcing security policies.
To configure a firewall in the lab environment:
- Enable the built-in firewall on the host operating system.
- Configure the firewall rules to allow legitimate traffic while blocking suspicious connections.
- Monitor firewall logs for suspicious activity.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS)
IDS/IPS systems monitor network traffic and host activity for suspicious patterns and anomalies. They detect and prevent intrusion attempts, such as unauthorized access, denial-of-service attacks, and malware infections.
To install and configure an IDS/IPS in the lab environment:
- Choose an open-source or commercial IDS/IPS solution.
- Install the IDS/IPS software on the host.
- Configure the IDS/IPS rules to monitor for specific threats and vulnerabilities.
Vulnerability Scanners
Vulnerability scanners identify security weaknesses and vulnerabilities in the host system and its software. They perform automated scans to detect missing patches, outdated software, and misconfigurations that could be exploited by attackers.
To use a vulnerability scanner in the lab environment:
- Download a reputable vulnerability scanner tool.
- Run the scanner against the host system.
- Review the scan results and prioritize the remediation of critical vulnerabilities.
Benefits of Security Tools
Implementing these security tools provides numerous benefits for host protection:
- Enhanced malware detection and prevention
- Protection against unauthorized access and network attacks
- Detection and prevention of security breaches and vulnerabilities
- Improved overall host security posture
Testing and Monitoring Host Security: Lab 14-1 Setup Host Security
Effective host security involves not only implementing security measures but also testing their efficacy and continuously monitoring the system for potential threats. This section will delve into the methods for testing host security configurations and vulnerabilities, emphasizing the significance of regular security monitoring and providing guidance on using security tools for monitoring and logging.
Testing Host Security Configurations and Vulnerabilities
Testing host security configurations and vulnerabilities is crucial to ensure that the system is secure and compliant with security standards. Several methods can be employed for this purpose, including:
- Vulnerability scanning:Automated tools scan the system for known vulnerabilities, such as missing security patches, outdated software, or insecure configurations.
- Configuration auditing:Tools compare the system’s configuration against a known secure baseline, identifying any deviations that could pose security risks.
- Penetration testing:Ethical hackers attempt to exploit vulnerabilities in the system, simulating real-world attacks to assess the system’s resilience.
Importance of Regular Security Monitoring
Regular security monitoring is essential for detecting and responding to security threats promptly. Continuous monitoring allows organizations to identify suspicious activities, such as unauthorized access attempts, malware infections, or system misconfigurations, before they can cause significant damage. By promptly addressing these issues, organizations can minimize the impact of security breaches and maintain system integrity.
Using Security Tools for Monitoring and Logging
Security tools play a vital role in monitoring and logging security events. These tools provide real-time monitoring, alerting, and logging capabilities, enabling organizations to detect and investigate security incidents effectively. Some commonly used security tools include:
- Intrusion detection systems (IDS):Monitor network traffic for suspicious activities and generate alerts when potential threats are detected.
- Security information and event management (SIEM) systems:Collect and analyze security logs from multiple sources, providing a centralized view of security events and facilitating incident response.
- Log management tools:Store and manage security logs, allowing organizations to review and analyze historical data for security audits and forensic investigations.
Documenting and Reporting Security Findings

Documenting and reporting security findings is crucial for effective security management. It ensures that identified vulnerabilities and threats are clearly communicated, allowing organizations to prioritize remediation efforts and improve their overall security posture.
A comprehensive security report should include the following key elements:
- Executive Summary:A brief overview of the key findings and recommendations.
- Scope:The boundaries and limitations of the security assessment.
- Methodology:The tools and techniques used to conduct the assessment.
- Findings:A detailed description of the identified vulnerabilities and threats, including their severity and potential impact.
- Recommendations:Specific actions that the organization should take to mitigate the identified risks.
- Appendix:Supporting documentation, such as scan results and vulnerability reports.
To ensure consistency and clarity, it is recommended to use a standardized template for documenting and reporting security findings. This template should include fields for each of the key elements listed above.
Key Questions Answered
What is the significance of Lab 14-1 setup host security?
Lab 14-1 provides a hands-on approach to understanding and implementing host security measures, equipping you with practical skills to safeguard your digital environment.
How does Lab 14-1 help me improve my host security?
Lab 14-1 guides you through the process of configuring security settings, installing security tools, and testing your defenses. By completing the lab, you’ll gain a comprehensive understanding of host security best practices.